| English | 简体中文 |
1001. Grid Illumination
Description
There is a 2D grid of size n x n where each cell of this grid has a lamp that is initially turned off.
You are given a 2D array of lamp positions lamps, where lamps[i] = [rowi, coli] indicates that the lamp at grid[rowi][coli] is turned on. Even if the same lamp is listed more than once, it is turned on.
When a lamp is turned on, it illuminates its cell and all other cells in the same row, column, or diagonal.
You are also given another 2D array queries, where queries[j] = [rowj, colj]. For the jth query, determine whether grid[rowj][colj] is illuminated or not. After answering the jth query, turn off the lamp at grid[rowj][colj] and its 8 adjacent lamps if they exist. A lamp is adjacent if its cell shares either a side or corner with grid[rowj][colj].
Return an array of integers ans, where ans[j] should be 1 if the cell in the jth query was illuminated, or 0 if the lamp was not.
Example 1:
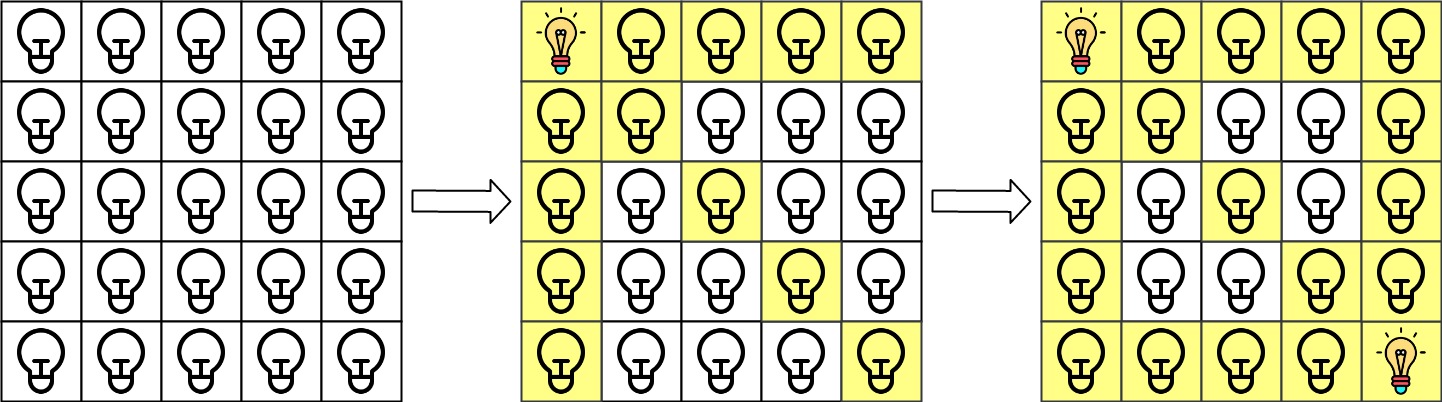
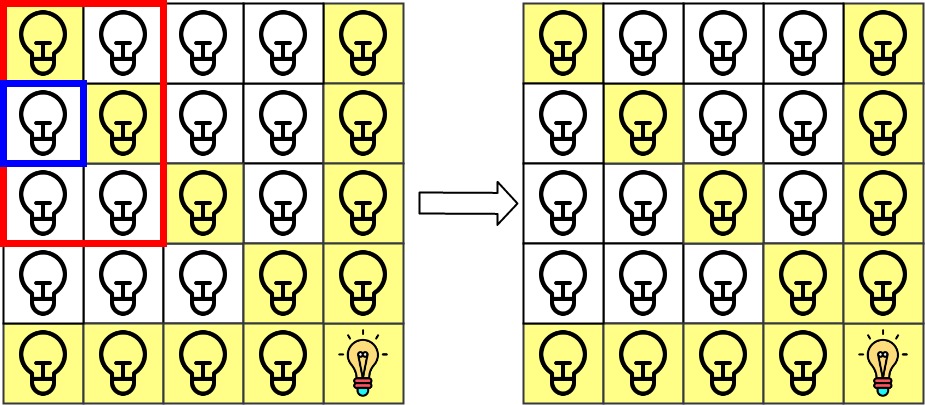
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: [1,0] Explanation: We have the initial grid with all lamps turned off. In the above picture we see the grid after turning on the lamp at grid[0][0] then turning on the lamp at grid[4][4]. The 0th query asks if the lamp at grid[1][1] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is illuminated, so set ans[0] = 1. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red square.The 1st query asks if the lamp at grid[1][0] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is not illuminated, so set ans[1] = 0. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red rectangle.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,1]] Output: [1,1]
Example 3:
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[0,4]], queries = [[0,4],[0,1],[1,4]] Output: [1,1,0]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1090 <= lamps.length <= 200000 <= queries.length <= 20000lamps[i].length == 20 <= rowi, coli < nqueries[j].length == 20 <= rowj, colj < n